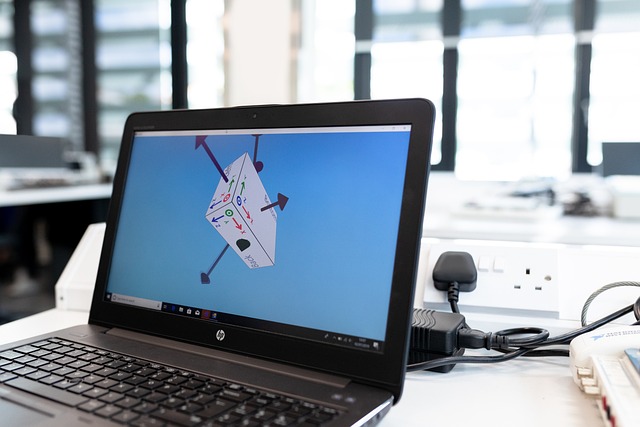
Choosing the right PLM software transforms product development by connecting teams, streamlining processes, and improving decision-making. Leading platforms like Siemens’ offer integrated solutions that boost efficiency across design, manufacturing, and lifecycle management. Understanding these tools helps businesses innovate faster, reduce costs, and scale effectively—making PLM software a pivotal step toward sustainable growth in competitive markets.
What is PLM Software and Why It Matters for Product Development
Understanding Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) software means grasping how businesses oversee a product from concept through retirement. At its core, PLM addresses the coordination of data, people, and processes so teams can innovate, collaborate, and maintain quality—no matter where they’re working. You can discover more by visiting this Direct access.
Have you seen this : Essential Elements for Developing Innovative AI-Driven Wearable Technology Applications
PLM shines when business challenges arise, such as data accessibility across global teams, real-time collaboration, and strict demand for product quality and compliance. With a centralized “source of truth,” organizations prevent errors caused by duplicates or outdated designs and streamline version control for smooth engineering handovers.
Modern PLM has transformed significantly: what started as CAD file management systems have evolved into cloud-based, integrated digital platforms supporting the complete value chain. Today’s solutions connect engineering tools, supply chain software, and manufacturing process integration in one cloud ecosystem, making cross-department sharing simple. PLM platforms, like those provided by Siemens, deliver tools for real-time product tracking, simulation and validation, secure collaboration, and enforced process standards—all while ensuring critical product and process data remain reliable and accessible.
This might interest you : Unlock the potential of linkedin api: a developer's guide
Cloud-based PLM’s agile frameworks let businesses respond quickly to market changes, boost innovation, and maintain competitive advantages without complex on-premise setups.
Core Features and Capabilities of PLM Software
PLM software centralizes product data management, underpinning a digital thread for transparency across the entire product lifecycle. This foundational approach allows businesses to maintain an accessible, accurate source of product information, minimizing confusion and improving operational alignment. Discovering the strength of a product data management overview, users experience direct control over information, benefiting from real-time product tracking and audit-ready documentation.
Modern PLM platforms champion engineering collaboration tools that break barriers between design, manufacturing, and supply chain teams—even when distributed globally. Secure versioning and revision control ensure every stakeholder operates with the latest product data, confidently supporting change management solutions without risking errors. Strong document management integration further safeguards sensitive IP, while enabling rapid responses to evolving project requirements.
Integration is core—API integrations and CAD integration capabilities connect PLM with ERP and supply chain systems. This seamless information flow powers optimized engineering workflows, reduces manual entry, and cuts down on costly miscommunications. With cloud-based lifecycle platforms, scalability and accessibility are vastly increased, ensuring organizations can adapt quickly, support remote teams, and keep pace with rapid product innovation.
Comparing Leading PLM Solutions and Industry Applications
Teamcenter platform features, Windchill system overview, and Dassault lifecycle solutions set the industry benchmark for product lifecycle management concepts. Siemens lifecycle integration excels by connecting digital product development across mechanical, electrical, and software domains. This alignment enables manufacturing process integration and seamless supply chain coordination software critical for high-complexity sectors.
SolidWorks lifecycle add-ons and SAP lifecycle modules are recognized for strong configuration management systems and engineering collaboration tools, supporting robust requirements management software for discrete manufacturing. In life sciences, medical device lifecycle software such as Riffyn X enhances real-time product tracking and traceability, ensuring strict compliance and quality assurance workflows.
Industry-specific lifecycle applications are tailored for automotive lifecycle platforms, apparel and garment lifecycle systems, and aerospace product management. For example, Centric software for apparel and fashion industry lifecycle management delivers role-based access controls, rapid version control in product design, and intuitive document management integration to address fast-paced trends.
Comparative reviews of lifecycle systems emphasize cloud-based lifecycle platforms—like Oracle Agile lifecycle tools—offering scalable PLM architectures with extensive API integrations and lifecycle analytics and reporting. These tools underpin agile product lifecycle management by ensuring multi-site collaboration, advanced customization, and comprehensive support for digital transformation initiatives across industries.
Selecting and Implementing the Right PLM System for Your Business
Criteria for Evaluating PLM Platforms and Aligning with Business Needs
The most important criteria include supporting product lifecycle management concepts, enabling seamless engineering collaboration tools, and providing robust manufacturing process integration. Successful deployment is underpinned by ensuring the PLM system aligns with your digital product development goals and supports critical lifecycle management benefits. Platforms like Siemens Teamcenter and PTC Windchill deliver advanced collaboration and real-time product tracking, promoting agile communication and a unified digital product data management overview. An effective solution must seamlessly handle bill of materials management, document management integration, and configuration management systems.
Implementation Best Practices, Scalability, and User Training for Adoption Success
For adoption, implementation strategies should prioritize scalable PLM architectures and thorough user training and support. Early migration and upgrade paths simplify transitions, while cloud-based lifecycle platforms enable scalable growth as business needs evolve. Training resources and tutorials foster user confidence, crucial for maximizing lifecycle analytics and reporting. Multi-site collaboration, strong API integrations, and simulation and validation tools ensure broad usability and future-ready digital transformation impact.
Cost Considerations, ROI Evaluation, and Emerging Trends in PLM Software
When assessing total cost of ownership insights, look beyond basic subscription and licensing models. Analyze ROI of lifecycle software, focusing on how lifecycle software demos and free and trial software options illuminate value. Current trends—like AI-driven lifecycle analytics, IoT data utilization, and sustainable engineering—will further shape product roadmap planning and ongoing lifecycle system customization.